The LoK-Med project, “The Lands of Kings and Emperors in a Mediterranean region (9th-11th centuries). Fiscal estates and economic growth”, was selected in 2017 by the MIUR within the FARE Program, in order to increase research excellence in Italy. Project funding began in 2018 and the program is scheduled to end in 2022.
LoK-Med is a complementary project to nEU-Med, aimed at strengthening a specific line of research through the application of innovative and multidisciplinary methodologies to the study of historical landscapes in the sample area of the ERC project.
Survey activities are coordinated by the Department of Historical Sciences and Cultural Heritage of the University of Siena, in collaboration with the Departments of Earth Sciences and Biotechnology, Chemistry and Pharmacy. LoK-Med was developed by the scientific team of the nEU-Med project.
Its multidisciplinary approach includes geoarchaeological, geochemical and archaeobotanical analyses for the reconstruction of ancient anthropic landscapes, their physiognomy and the productive activities that characterized them.

Through remote sensing techniques aimed at identifying specific elements of the landscape, such as ancient agricultural terracing, changes in the use of agroforestry land, evidence related to mining, coalmines, settlements, roads and hydraulic systems, the project focuses on the great transformations the landscape underwent in the Early Middle Ages, when the stage was set for the successive economic development that invested most of Europe during the eleventh century.
Result dissemination is facilitated by the use of 3D modeling and historical landscape reconstruction.
In particular, the new databases acquired by the LoK-Med project include the following points:
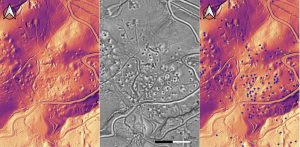
- The carrying out of high resolution LiDAR coverage (ground density 20 points/m²) of 22,000 hectares. This will offer both a useful and unique topographic and cartographic base, in addition to low resolution coverage currently acquired by the National Geoportal (MATTM). The base will be available online for multidisciplinary surveys through the provision of WMS (Web Map Service) and WCS (Web Coverage Service).
- Re-elaboration of the LiDAR data will further enrich the database related to the historical evolution of the anthropic and natural landscape, providing information that can also be used for landscape monitoring (hydrogeological risks, land management, forest coverage types) and the elaboration of future research projects.
- The three-dimensional modeling of historical landscapes will allow to acquire the necessary information that can also be applied in future research projects.
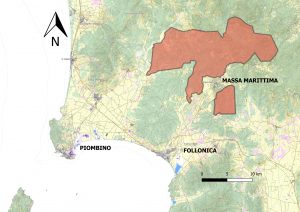
- The subsequent three-dimensional graphic modeling and historical reconstructions will provide the opportunity to develop a concept, presenting the main transformations of the territory to the general public. This research product can also be linked to future projects of valorization, towards which local authorities in the territories of the ERC nEU-Med project have already expressed interest (Parchi Val di Cornia; Geoparco delle Colline Metallifere, municipalities of: Piombino, Scarlino, Massa Marittima, Monterotondo Marittimo).